The Assam Higher Secondary Education Council, AHSEC has released the Model Question Paper for Chemistry for the HS Final Examination 2026. In this article we have extracted the Model Questions of AHSEC HS 2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 10 – Biomolecules. It may help the students to prepare for the examination.
Chapter 10 – Biomolecules : Model Questions
1. Assertion (A): Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. 1
Reason (R): Sucrose has glycosidic linkage.
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(iii) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is incorrect statement.
(iv) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is correct statement.
2. Give the plausible explanation for the following:
(a) Glucose doesn’t give 2, 4-DNP test.
(b) The two strands in DNA are not identical but are complementary.
(c) Starch and cellulose both contain glucose unit as monomer, yet they are structurally different.
3. Organic compounds containing amine as functional group are present in a vivid variety of compounds, namely amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, DNA, alkaloids, dyes, etc. Drugs including nicotine, morphine, codeine and heroin, etc. which have physiological effects on humans also contain amino group in one form or another. Amines are basic because of the presence of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen. Addition of nitrogen into an organic framework leads to the formation of two families of molecules, namely amines and amides. As chemistry students, we must appreciate the versatility of nitrogen.
1. What are amino acids?
2. Why are amino acids amphoteric?
3. Give one point of difference between acidic and basic amino acid.
4. What are essential amino acids?
5. Name the linkage formed when carboxyl end of one amino acid condenses with amino end of other amino acid?
5. Assertion (A): Albumin is a globular protein.
Reason (R): Polypeptide chain coils around to give a straight chain.
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(iii) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is incorrect statement.
(iv) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is correct statement.
6. Peptide linkage is present in
(A) Carbohydrates
(B) Vitamins
(C) Proteins
(D) Rubber
7. Define the following terms:
(i) Oligosaccharides
(ii) Invert sugar
8. Write the name of component of starch which is water soluble.
9. An a -helix is a structural feature of
(a) Sucrose
(c) Nucleotides
(b) Polypeptides
(d) Starch
10. Write the reactions showing the presence of following in structure of glucose:
(i) a carbonyl group
(ii) Straight chain with six carbon atoms
10. Amino acids are-
(a) acidic
(b) basic
(c) amphoteric
(c) neutral
11. Differentiate between following:
(i) Amylose and Amylopectin
(ii) Globular protein and Fibrous protein
(iii) Nucleotide and Nucleoside
12. Which of the following is a disaccharide?
(A) Starch
(B) Maltose
(C) Fructose
(D) Glucose
13. Which of the following terms is correct about enzymes?
(A) Proteins
(B) Dinucleotides
(C) Nucleic acids
(D) Hormones
14. Which of the following B group vitamins can be stored in our body?
(A) Vitamin B-1
(B) Vitamin B-2
(C) Vitamin B-6
(D) Vitamin B-12
15. Assertion (A): Vitamin D can be stored in our body.
Reason (R): Vitamin D is a water-soluble vitamin.
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(iii) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is incorrect statement.
(iv) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is correct statement.
16. Assertion (A): Vitamin D can be stored in our body.
Reason (R): Vitamin D is a water-soluble vitamin.
17. The glycosidic linkage involved in linking the glucose units in amylase part of starch is
(a) C1 – C6 a linkage
(b) C1 – C6 b linkage
(c) C1 – C4 a linkage
(d) C1 – C4 b linkage
18. An a -helix is a structural feature of:
(a) Sucrose
(b) Starch
(c) Polypeptides
(d) Nucleotides
19.
(a) Write chemical reaction to show that open structure of D-glucose contains the straight chain.
(b) What type of linkage is responsible for the formation of protein?
20.
(a) What are the hydrolysis products of
(i) Lactose,
(ii) Maltose?
(b) Give the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose.
21. An a -helix is a structural feature of
(a) Sucrose
(b) Polypeptides
(c) Nucleotides
(d) Starch
22. Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. They are also called saccharides. All those carbohydrates which reduce Fehling’s solution and Tollen’s reagent are referred to as reducing sugars. Glucose, the most important source of energy for mammals, is obtained by the hydrolysis of starch. Vitamins are accessory food factors required in the diet. Proteins are the polymers of a -amino acids and perform various structural and dynamic functions in the organisms. Deficiency of vitamins leads to many diseases.
Answer the following:
(a) The penta-acetate of glucose does not react with Hydroxylamine. What does it indicate?
(b) Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body?
(c) Define the following as related to proteins
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Denaturation
23. Define the following as related to carbohydrates:
(i) Anomers (ii) Glycosidie linkage
24. On hydrolysis, which of the following carbohydrates gives only glucose?
(a) Starch
(b) Fructose
(c) Lactose
(d) Sucrose
25. Which of the following vitamins is water soluble?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin D
(c) Vitamin E
(d) Vitamin C
26. Write the structure of product when D-Glucose reacts with the following: (any three)
(a) HI
(b) Conc. HNO3
(c) Br2 water
(d) HCN
27. Which of the following structures represents a -D-glucose?
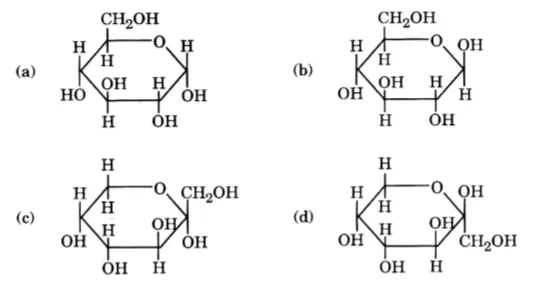
28. On hydrolysis, which of the following carbohydrates gives only glucose?
(a) Maltose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Lactose
(d) Galactose
29. Deficiency of which of the following vitamins causes Pernicious anaemia? (a) Vitamin B1
(b) Vitamin B2
(c) Vitamin B6 (
d) Vitamin B12
30. Living systems are made up of various complex biomolecules like carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, etc. Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or molecules which provide such units on hydrolysis. They are broadly classified into three groups – monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are held together by glycosidic linkages to form disaccharides like sucrose, maltose or polysaccharides like starch and cellulose. Another biomolecule: proteins are polymers of a -amino acids which are linked by peptide bonds. Ten amino acids are called essential amino acids. Structure and shape of proteins can be studied at four different levels i.e. primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary, each level being more complex than the previous one.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What is the difference between a glycosidic linkage and peptide linkage?
(ii) Which amino acids are called essential amino acids?
(iii)What are the common types of secondary structures of proteins? Write any two forces which stabilise the secondary and tertiary structures of protein.
OR
(iii)Define denaturation of protein with an example. During denaturation which structures of protein lose their biological activity?
31. Hydrolysis of sucrose is called
(a) inversion
(b) hydration
(c) esterification
(d) saponification
32. Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of a -amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bond.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
33. Give the reaction of glucose with hydrogen cyanide. Presence of which group is confirmed by this reaction?
34. Give reasons for any 3 of the following observations:
(a) Penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(b) Amino acids behave like salts.
(c) Water soluble vitamins must be taken regularly in diet.
(d) The two strands in DNA are complimentary to each other.
35. The helix structure of proteins is stabilized by:
(a) peptide bonds
(b) disulphide bonds
(c) hydrogen bonds
(d) Van der Waals forces
36. The deficiency of which Vitamin causes rickets?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
37. Oligosaccharides on hydrolysis could yield:
(a) 3 to 9 monosaccharides
(b) 4 to 10 monosaccharides
(c) more than 10 monosaccharides
(d) 3 to 10 monosaccharides
38. Carbohydrates are broadly classified into three groups:
Monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are held together by glycosidic linkages to form disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Proteins which contain only a -amino acids are called simple proteins. Proteins get denatured if subjected to change in temperature or pH.
Answer the following:
(i) What is the difference between glycosidic linkage and peptide linkage?
(ii) What is the effect of denaturation on the structures of protein?
(iii) Define the following terms:
(1) Essential amino acids
(2) Anomers
OR
(iii)What are the hydrolysis products of:
(1) Sucrose
(2) Lactose
39. Two among the three components of DNA are b -D-2-deoxyribose and a heterocyclic base. The third component is:
(A) Adenine
(B) Phosphoric acid
(C) Sulphuric acid
(D) Uracil
40. Which functional groups of glucose interact to form cyclic hemiacetal leading to pyranose structure?
(A) Aldehyde group and hydroxyl group at C-4
(B) Aldehyde group and hydroxyl group at C-5
(C) Ketone group and hydroxyl group at C-4
(D) Ketone group and hydroxyl group at C-5
41. What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
(a) HI (b) Conc. HNO3
42. Answer the following:
(a) What is peptide linkage?
(b) What type of bonds hold a DNA double helix together?
(c) Which one of the following is a polysaccharide? Sucrose, Glucose, Starch, Fructose
(d) Give one example each for water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins.
43. The vitamin which plays an important role in coagulating blood is
(A) Vitamin A
(B) Vitamin E
(C) Vitamin D
(D) Vitamin K
